Sanjay Kumar Madria
Curators' Distinguished Professor
Computer Science
- madrias@mst.edu
- Phone: (573) 341-4856
- 319 Computer Science Building
Publications:
Personal Website:
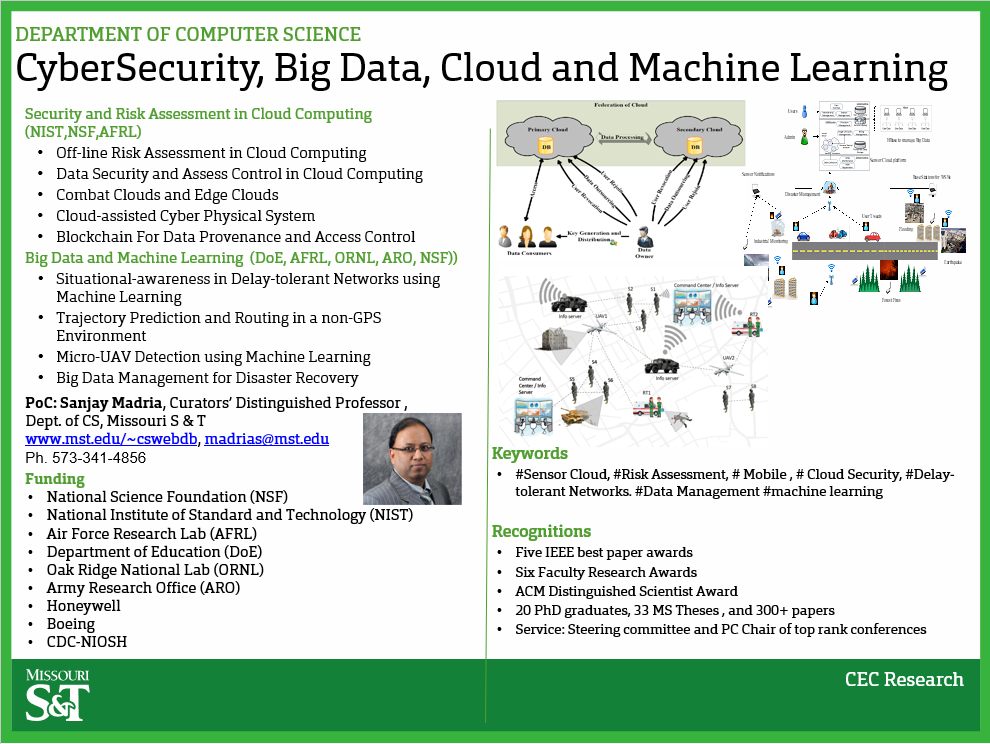
- Secure Sensor Cloud
- Off-line Risk Assessment of Cloud Service Providers
- ESCAPE of Big Data for Disaster Applications
- Opportunistic Mission Critical Information Dissemination
Secure Sensor Cloud
Secure Sensor Cloud
INVESTIGATORS
Sanjay Madria (Dept. of Computer Science, 573-341-4856)
FUNDING SOURCE
NIST
PROJECT DESCRIPTION
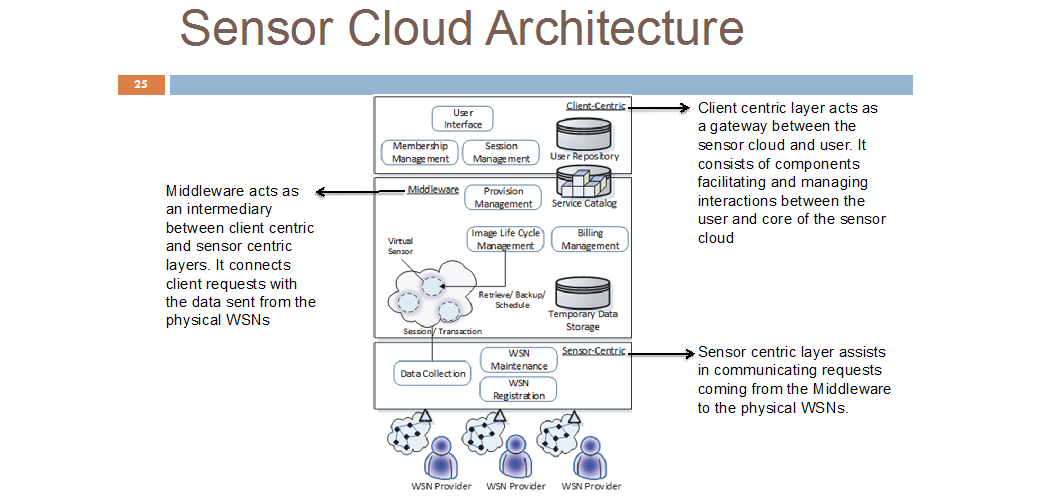
In sensor cloud, the security of a sensor network cannot be assessed by simply considering the feasible set of attacks in isolation. To accurately determine the security of a network, one must be able to determine the interdependencies between these attacks and how they can be exploited to execute a multistage attack on the sensor networks. These situations demand the need of risk assessment for a sensor network. Risk assessment using attack graphs will help the security administrators visualize the interdependencies between the various attacks and how they can be used in combination to cause more damage to the network.
With respect to sensor clouds which has two layers, a physical sensor network to perform the actual tasks and a virtualization of this sensor network which is hosted at the cloud platform, in this project, we will design risk modeling on both of these layers with the help of attack graphs and assess the interdependencies between the possible set of attacks on both of these layers and integrate them to assess the overall security of the sensor cloud platform. Attack graphs in a combination with principles like Bayesian networks will also help in estimating which of the given attack sets are most feasible to execute on the physical sensor layer and how that will affect the virtual layer on the cloud platform. We will also be able to determine the cost of implementing the security measures using the aforementioned principles, which will help in implementing network hardening strategies for the sensor cloud platform.
PUBLICATIONS
- “Risk Assessment in a Sensor Cloud Framework Using Attack Trees,” Amartya Sen and Sanjay Madria, in IEEE Transaction on Service Computing (TSC), 2016.
- “Security and Risk Assessment in the Cloud,” Sanjay Madria, IEEE Computer, Volume: 49, Issues: 9, Sept. 2016, IEEE Computer, 2016
- “A Sensor Cloud Test-bed for Multi-Model and Multi-User Sensor Applications,” Sanjay Madria, Amartya Sen, Rashmi Dalvi, in IEEE WCNC, 2016.
- “Distributed Attribute Based Access Control of Aggregated Data in Sensor Clouds,” Vimal Kumar and Sanjay Madria, in IEEE proceedings in 34th Symposium on Reliable Distributed Systems (SRDS 2015) Montreal, Canada. IEEE Best Paper Award.
- “Energy-Efficient Scheduling of Fine-granularity Tasks in a Sensor Cloud,” Rashmi Dalvi and Sanjay Madria, in proceedings of 20th International Conference on Database Systems for Advanced Applications, Hanoi, Vietnam, April, 2015.
- “Efficient and Secure Code Dissemination in Sensor Clouds,” Vimal Kumar and Sanjay Madria, in the Proceedings of 15th IEEE Conference on Mobile Data Management, Brisbane, Australia, 2014.
Off-line Risk Assessment of Cloud Service Providers
Off-line Risk Assessment of Cloud Service Providers
 INVESTIGATORS
INVESTIGATORS
Sanjay Madria (Dept. of Computer Science, 573-341-4856)
FUNDING SOURCE
NSF
PROJECT DESCRIPTION
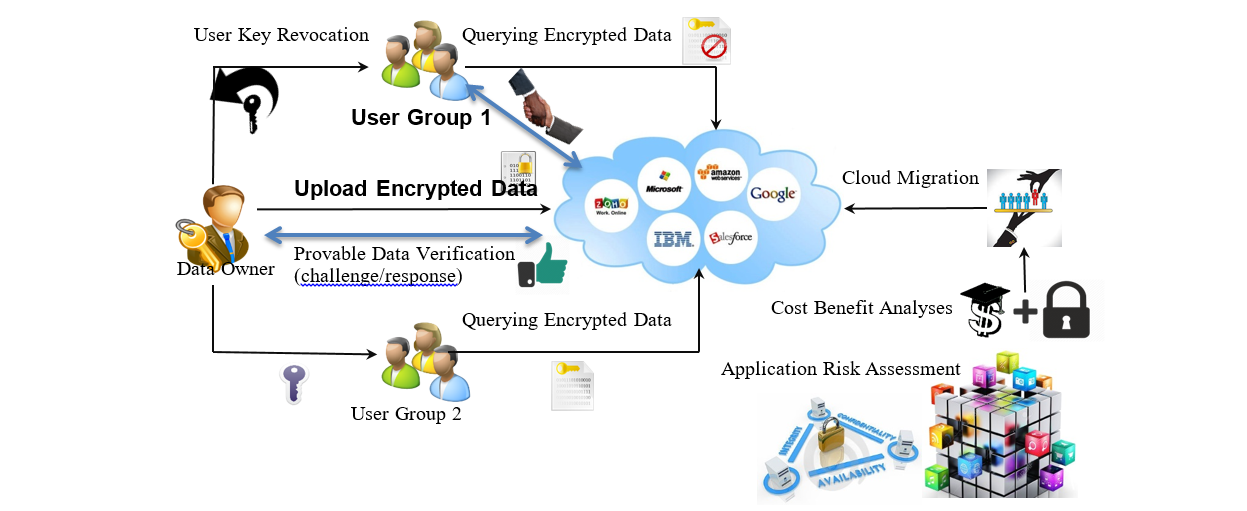
The acceptance of the cloud as an infrastructure to host applications is a growing trend. Facilitating and hosting applications on the cloud reduces support and maintenance costs. However, concerns about the security of these applications is one of the primary reasons organizations avoid complete adoption of cloud services. Although cloud service providers (CSPs) offer standard security, they don't address security with respect to application's security requirements. This project aims to propose an offline risk-assessment framework to evaluate the security offered by a CSP from the perspective (security needs) of an application to be migrated to it. Once the most secure CSP is identified for a given application, the proposed framework performs a cost-benefit trade-off analysis in terms of the security dispensed and service costs to support the formation of an ideal cloud migration plan.
PUBLICATIONS
- “Off-line Risk Assessment of Cloud Service Provider,” Amartya Sen and Sanjay Madria, in IEEE Cloud Computing, 2(3): 50-57 (2015).
- “Off-line Risk Assessment of Cloud Service Providers,” Amartya Sen and Sanjay Madria, in the Proceedings of Second IEEE International Workshop on Cloud Security Auditing, Alaska, USA, July 2014.
ESCAPE of Big Data for Disaster Applications
ESCAPE: Efficient and Scalable Collection, Analytics and Processing of Big Data for Disaster Applications
INVESTIGATORS
Sanjay Madria (Dept. of Computer Science, 573-341-4856)
FUNDING SOURCE
NSF
PROJECT DESCRIPTION
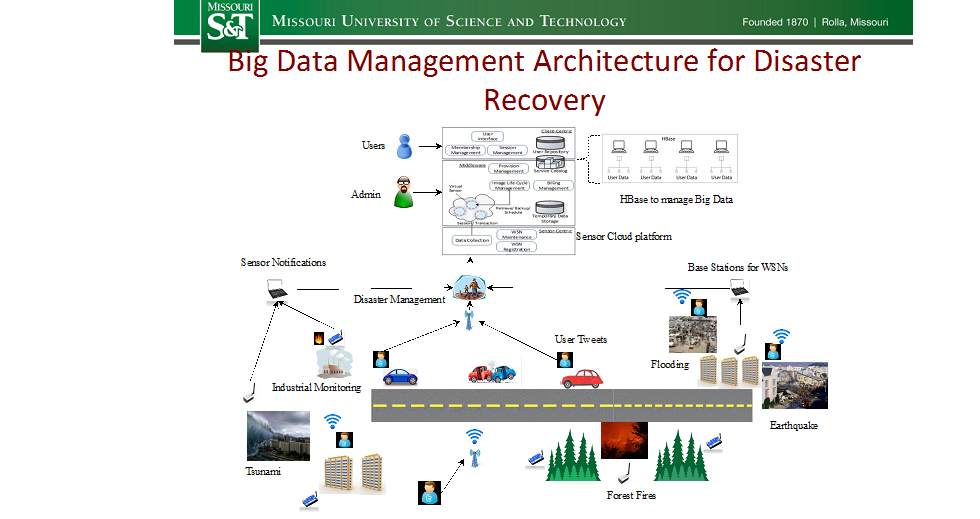
Efficient management of natural and man-made disasters poses technical challenges like energy efficient collection of sensor data, optimizing the network bandwidth, faster analysis of the past data/events and dissemination of timely and correct information using Sensor cloud architecture to the people involved in decision-making.
The outcomes from this project is to assist human operators in their disaster management coordination and planning like directing a medical physician’s team to their nearest cluster of affected people in a region and administer medications as necessary or finding a safe route for evacuation of affected people. Sensor data integrated with microblogs such as Tweets help identifying some local events and people sentiments, which is significantly useful in handling/understanding disaster situations. It will also benefit other applications such as real-time tracking of road/driving conditions in vehicular networks.
PUBLICATIONS
- “Top-k Query Processing in Mobile-P2P Networks using Economic Incentive Schemes,” Nilesh Padhariya, Anirban Mondal, Sanjay Kumar Madria and Masaru Kitsuregawa, in Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications Springer-verlag, Vol. 9, Issue. 4, 2016.
- “Top-K with Diversity-M Data Retrieval in Wireless Sensor Networks,” Kiran Kumar Puram and Sanjay Madria, to appear in 17th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management, 2016.
Opportunistic Mission Critical Information Dissemination
Opportunistic Mission Critical Information Dissemination using Incentives in Delay (Disruption) Tolerant Networks
INVESTIGATORS
Sanjay Madria (Dept. of Computer Science, 573-341-4856)
FUNDING SOURCE
AFRL
PROJECT DESCRIPTION
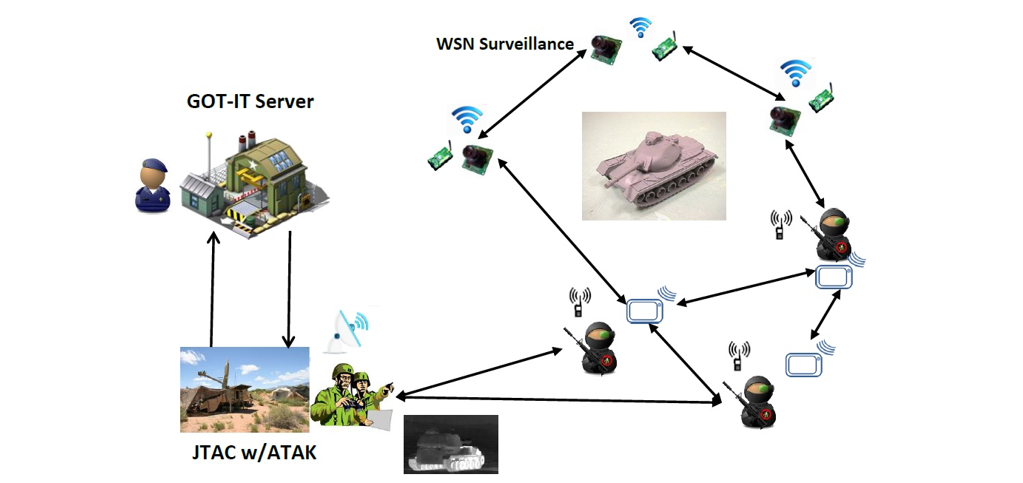
In this project, the focus is to enhance the advanced Information Management (IM) services. There is a need to further improve the exchange of information through message delivery between enterprise and the tactical edge networks and applications, the information management services need to be capable of operating in contested/congested environments and be built upon disruption and fault tolerant techniques and technologies. The objective is to develop and demonstrate opportunistic delay or disruption tolerant networks (DTNs) for rapid access to ISR and to support hybrid and decentralized IM services across enterprise and tactical network infrastructures to enable effective information exchange for shared situational awareness. This will bridge the gap between low bandwidth and high bandwidth data producers and consumers and provide the ability to discover and share data across disparate systems under GOT-IT architecture. In this environment, thus, priority of messages, intelligent caching of mission critical messages using incentives, higher message delivery of unique messages as well as reducing the network traffic is very important for the mission.
PUBLICATIONS
- “ChitChat: An Effective Message Delivery Method in Sparse Pocket-Switched Networks,” Doug McGeehan, Dan Lin and Sanjay Madria, to appear in 36th IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS 2016), Nara, Japan.


Follow Intelligent Systems Center